我们希望研究1978车辆数据中两个变量油耗和重量之间的关系。
. use auto_zh, clear
首先我们检查油耗和重量的变量描述和摘要统计数据。
. describe 油耗 重量
storage display value
variable name type format label variable label
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
油耗 float %9.0g 油量消耗(公升每一百公里)
重量 float %8.0gc 重量(公斤)
. summarize 油耗
Variable | Obs Mean Std. Dev. Min Max
-------------+---------------------------------------------------------
油耗 | 74 5.01928 1.279856 2.439024 8.333333
从摘要统计数据看出,变量油耗的最小值2.44,最大值8.33,极差5.89。
. summarize 重量
Variable | Obs Mean Std. Dev. Min Max
-------------+---------------------------------------------------------
重量 | 74 1369.603 352.5288 798.3219 2195.385
从摘要统计数据看出,变量重量的最小值798.32,最大值2195.39,极差1397.06。
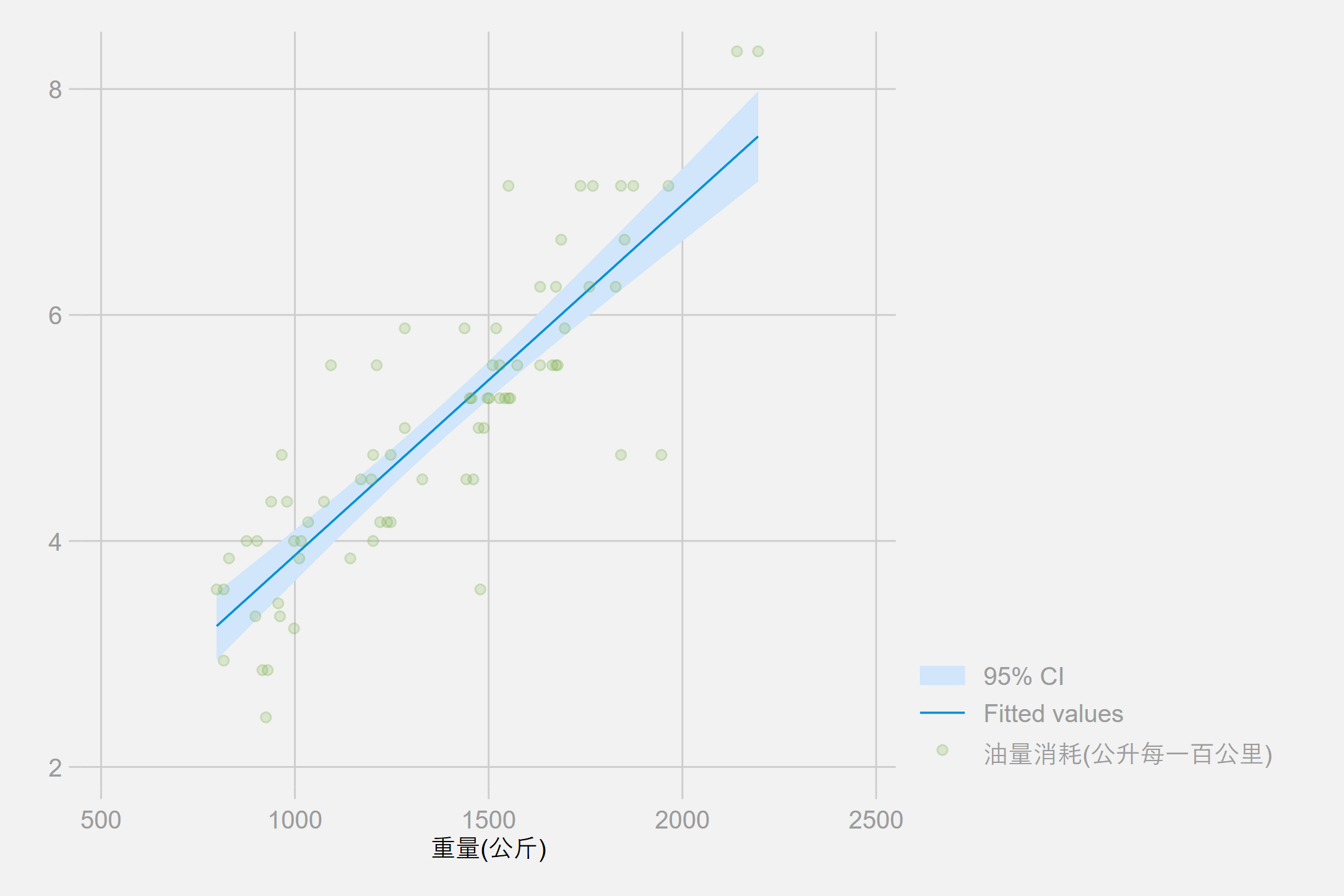
. twoway lfitci 油耗 重量 || scatter 油耗 重量, mcolor(%20) scheme(538)

我们在油耗和重量的散点图上叠加拟合值与均值的置信区间。
. regress 油耗 重量
Source | SS df MS Number of obs = 74
-------------+---------------------------------- F(1, 72) = 194.71
Model | 87.2964971 1 87.2964971 Prob > F = 0.0000
Residual | 32.2797637 72 .448330051 R-squared = 0.7300
-------------+---------------------------------- Adj R-squared = 0.7263
Total | 119.576261 73 1.63803097 Root MSE = .66957
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
油耗 | Coef. Std. Err. t P>|t| [95% Conf. Interval]
-------------+----------------------------------------------------------------
重量 | .003102 .0002223 13.95 0.000 .0026589 .0035452
_cons | .7707669 .3142571 2.45 0.017 .1443069 1.397227
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
线性回归结果显示重量每增加一百公斤,每百公里油耗增加 0.3102公升, 可由模型解释的观察到的方差量为 73%.
. _coef_table, markdown
| 油耗 | Coef. | Std. Err. | t | P>|t| | [95% Conf. Interval] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重量 | .003102 | .0002223 | 13.95 | 0.000 | .0026589 | .0035452 |
| _cons | .7707669 | .3142571 | 2.45 | 0.017 | .1443069 | 1.397227 |
quietly regress 油耗 重量 变速比 转弯半径
estimates store 模型1
quietly regress 油耗 重量 变速比 转弯半径 国籍
estimates store 模型2
estimates table 模型1 模型2, b(%7.4f) stats(N r2_a) star
. estimates table 模型1 模型2, varlabel b(%7.4f) stats(N r2_a) star markdown
| Variable | 模型1 | 模型2 |
|---|---|---|
| 重量(公斤) | 0.0030*** | 0.0028*** |
| 变速比 | 0.1706 | -0.3367 |
| 转弯半径(米) | 0.0798 | 0.2010 |
| 国籍 | 0.8650*** | |
| Constant | -0.5814 | -0.4661 |
| N | 74 | 74 |
| r2_a | 0.7218 | 0.7637 |
legend: * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001
eststo : quietly regress 油耗 重量 变速比 转弯半径
eststo : quietly regress 油耗 重量 变速比 转弯半径 国籍
esttab using esttab_ex.html, label ///
width(80%) nogaps ///
mtitles("模型1" "模型2") ///
title(线性回归结果)
| (1) | (2) | |
| 模型1 | 模型2 | |
| 重量(公斤) | 0.00301*** | 0.00278*** |
| (6.09) | (6.06) | |
| 变速比 | 0.171 | -0.337 |
| (0.64) | (-1.19) | |
| 转弯半径(米) | 0.0798 | 0.201 |
| (0.70) | (1.81) | |
| 国籍 | 0.865*** | |
| (3.66) | ||
| Constant | -0.581 | -0.466 |
| (-0.38) | (-0.33) | |
| Observations | 74 | 74 |
|
t statistics in parentheses
* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 | ||
The community-contributed esttab is available on the Boston College Statistical Software Components (SSC) archive; see ssc install for details.